

Causes | Anatomy | Diagnosis | Treatment | Rehabilitation
Achilles tendon rupture is when the achilles tendon breaks. The achilles is the most commonly injured tendon. Rupture can occur while performing actions requiring explosive acceleration, such as pushing off or jumping. The male to female ratio for Achilles tendon rupture varies between 7:1 and 4:1 across various studies.
 The achilles tendon
|
The Achilles tendon is most commonly injured by sudden plantarflexion or dorsiflexion of the ankle, or by forced dorsiflexion of the ankle outside its normal range of motion.
Other mechanisms by which the Achilles can be torn involve sudden direct trauma to the tendon, or sudden activation of the Achilles after atrophy from prolonged periods of inactivity. Some other common tears can occur from overuse while participating in intense sports. Twisting or jerking motions can also contribute to injury.
Fluoroquinolone antibiotics, famously ciprofloxacin, are known to increase the risk of tendon rupture, particularly Achilles.
People who commonly fall victim to Achilles rupture or tear include recreational athletes, people of old age, individuals with previous Achilles tendon tears or ruptures, previous tendon injections or quinolone use, extreme changes in training intensity or activity level, and participation in a new activity.
Most cases of Achilles tendon rupture are traumatic sports injuries. The average age of patients is 29–40 years with a male-to-female ratio of nearly 20:1. Fluoroquinoloneantibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin, and glucocorticoids have been linked with an increased risk of Achilles tendon rupture. Direct steroid injections into the tendon have also been linked to rupture.
Quinolone has been associated with Achilles tendinitis and Achilles tendon ruptures for some time. Quinolones are antibacterial agents that act at the level of DNA by inhibiting DNA Gyrase. DNA Gyrase is an enzyme used to unwind double stranded DNA which is essential to DNA Replication. Quinolone is specialized in the fact that it can attack bacterial DNA and prevent them from replicating by this process, and are frequently prescribed to the elderly.
The Achilles tendon is the strongest and thickest tendon in the body, connecting the gastrocnemius, soleus and plantaris to the calcaneus. It is approximately 15 centimeters (5.9 inches) long and begins near the middle portion of the calf. Contraction of the gastrosoleus plantarflexes the foot, enabling such activities as walking, jumping, and running. The Achilles tendon receives its blood supply from its musculotendinous junction with the triceps surae and its innervation from the sural nerve and to a lesser degree from the tibial nerve.



Diagnosis is made by clinical history; typically people say it feels like being kicked or shot behind the ankle. Upon examination a gap may be felt just above the heel unless swelling has filled the gap and the Simmonds' test (aka Thompson test) will be positive; squeezing the calf muscles of the affected side while the patient lies prone, face down, with his feet hanging loose results in no movement (no passive plantarflexion) of the foot, while movement is expected with an intact Achilles tendon and should be observable upon manipulation of the uninvolved calf. Walking will usually be severely impaired, as the patient will be unable to step off the ground using the injured leg. The patient will also be unable to stand up on the toes of that leg, and pointing the foot downward (plantarflexion) will be impaired. Pain may be severe, and swelling is common.
Sometimes an ultrasound scan may be required to clarify or confirm the diagnosis. MRI can also be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Musculoskeletal ultrasonography can be used to determine the tendon thickness, character, and presence of a tear. It works by sending extremely high frequencies of sound through the body. Some of these sounds are reflected back off the spaces between interstitial fluid and soft tissue or bone. These reflected images can be analyzed and computed into an image. These images are captured in real time and can be very helpful in detecting movement of the tendon and visualising possible injuries or tears. This device makes it very easy to spot structural damages to soft tissues, and consistent method of detecting this type of injury. This imaging modality is inexpensive, involves no ionizing radiation and, in the hands of skilled ultrasonographers, may be very reliable.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used to discern incomplete ruptures from degeneration of the Achilles tendon, and MRI can also distinguish between paratenonitis, tendinosis, and bursitis. This technique uses a strong uniform magnetic field to align millions of protons running through the body. these protons are then bombarded with radio waves that knock some of them out of alignment. When these protons return they emit their own unique radio waves that can be analysed by a computer in 3D to create sharp cross sectional image of the area of interest. MRI can provide unparalleled contrast in soft tissue for an extremely high quality photograph making it easy for technicians to spot tears and other injuries.
Radiography can also be used to indirectly identify Achilles tears. Radiography uses X-rays to analyse the point of injury. This is not very effective at identifying injuries to soft tissue. X-rays are created when high energy electrons hit a metal source. X-ray images are acquired by utilising the different attenuation characteristics of dense (e.g. calcium in bone) and less dense (e.g. muscle) tissues when these rays pass through tissue and are captured on film. X-rays are generally exposed to optimise visualisation of dense objects such as bone while soft tissue remains relatively undifferentiated in the background. Radiography has little role in assessment of Achilles' tendon injury and is more useful for ruling out other injuries such as calcaneal fractures.
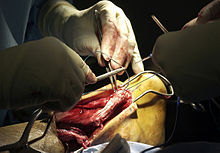
Treatment options for an Achilles tendon rupture include surgical and non-surgical approaches.
There are two different types of surgeries:
During an open surgery an incision is made in the back of the leg and the Achilles tendon is stitched together. In a complete or serious rupture the tendon of plantaris or another vestigial muscle is harvested and wrapped around the Achilles tendon, increasing the strength of the repaired tendon. If the tissue quality is poor, e.g. the injury has been neglected, the surgeon might use a reinforcement mesh (collagen, Artelon or other degradable material).
In percutaneous surgery, the surgeon makes several small incisions, rather than one large incision, and sews the tendon back together through the incision(s). Surgery may be delayed for about a week after the rupture to let the swelling go down. For sedentary patients and those who have vasculopathy or risks for poor healing, percutaneous surgical repair may be a better treatment choice than open surgical repair.
There are three things that need to be kept in mind while rehabilitating a ruptured Achilles:
To briefly summarize the steps of rehabilitating a ruptured Achilles tendon, you should begin with range of motion type stretching. This will allow the ankle to get used to moving again and get ready for weight bearing activities. Then there is functional strength, this is where weight bearing should begin in order to start strengthening the tendon and getting it ready to perform daily activities and eventually in athletic situations.
|
Page Content |